
一、看了许久的单词翻译大概知道啥意思了
Given:
start ="hit"end ="cog"dict =["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]变换一个单词并且在字典中,然后匹配到结尾的单词。
我觉得网上看的那个变换26个字母有点蠢啊。
二、思路
突然发现这样做可不可以。根据终点反推符合的单词,依次反推。
开始的地方是固定的匹配的单词也是固定的。
两处匹配就是一条通路
总的思路来说就是这样的了。
2.1 由结尾推到出上一个层次的数据。相同层次的转换忽略掉
一直到开始能够匹配的数据结束 这是一条通路
2.2这样有个问题就是例如下面的hot 可以被重复利用被忽略了。
2.3写完后发现dot和lot也是一对基友
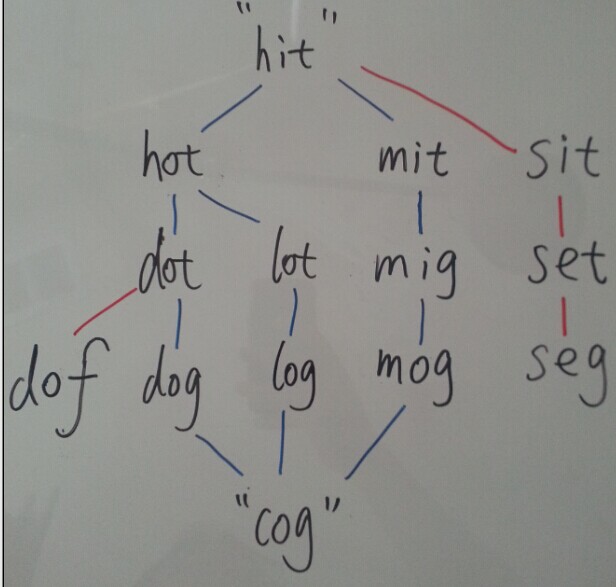
现在改进应该是如果下一个层次的数据,也可以被同层次的数据再一次利用那么这个数据也应该被保留
三、明天思考下程序
这个程序没有解决问题
package com.stx.test;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Stack;/** * 单词搜索 * @author K-BIRD */public class WordSearchTwo { private String start="hit"; private String end="cog";// private String dictArray[]={"hot","dot","dog","lot","log"}; private String dictArray[]={"hot","dot","dog","lot","log","dof","mit","sit","set","mog","mig","seg","nax","max"}; private ArrayList useList=new ArrayList (); private ArrayList headMatchList; private Stack pathStack=new Stack (); /** * 获取一个匹配的字符串,但是不包含已经存在的 */ public ArrayList getMatchStr(String str){ if(null==str)return null; ArrayList matchList=new ArrayList (); for(String s:dictArray){ if(s.length()!=str.length()||useList.contains(s)) continue; int count=0; for(int i=0;i temp=this.getMatchStr(str); if(temp==null||temp.isEmpty()){ pathStack.clear(); return; } for(String s:temp){ findPath(s); } } public static void main(String[] args) { WordSearchTwo wst=new WordSearchTwo(); wst.getHeadMatch(); wst.findPath(wst.end); }} 四、最后修改处理结果
思路:获取所节点以及匹配的孩子节点
卡在那个结束上和堆栈的打印上了
import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Set;import java.util.Stack;/** * 单词搜索 * @author K-BIRD */public class SearchWordTwo3 { private String start="hit"; private String end="cog";// private String dictArray[]={"hot","dot","dog","lot","log"}; private String dictArray[]={"hot","dot","dog","lot","log","dof","mit","sit","set","mog","mig","seg","nax","max"};//这里记录个全路径来 private Map >path=new HashMap >(); private Stack result=new Stack (); /** * 寻找路径 */ public Set findChild(String seed){ if(null==seed)return null; Set childSeed=new HashSet (); for(String str:dictArray){ int count=0; if(str.equals(seed))continue; for(int i=0;i childSet=findChild(seed); if(childSet!=null&&childSet.size()>0){ this.path.put(seed, childSet); for(String str:childSet){ findAllChild(str); } } } public void print(String nowStr,String preSet){ //如果匹配了 this.result.add(nowStr); int count=0; for(int i=0;i nowResult=this.path.get(nowStr); if(nowResult==null||nowResult.size()==0){ if(!this.result.isEmpty()) this.result.pop(); return; } for(String str:nowResult){ //对称的 if(str.equals(preSet)) continue; //如果结果堆栈中包含结果也继续 if(!this.result.isEmpty()&&this.result.contains(str)) continue; print(str,nowStr); } //如果循环完了的话组后一个和后面的那个一样的 if(!this.result.isEmpty()) this.result.pop(); } public static void main(String[] args) { SearchWordTwo3 swt3=new SearchWordTwo3(); swt3.findAllChild(swt3.end); swt3.print(swt3.end,null); }} 